Asphalt Calculator
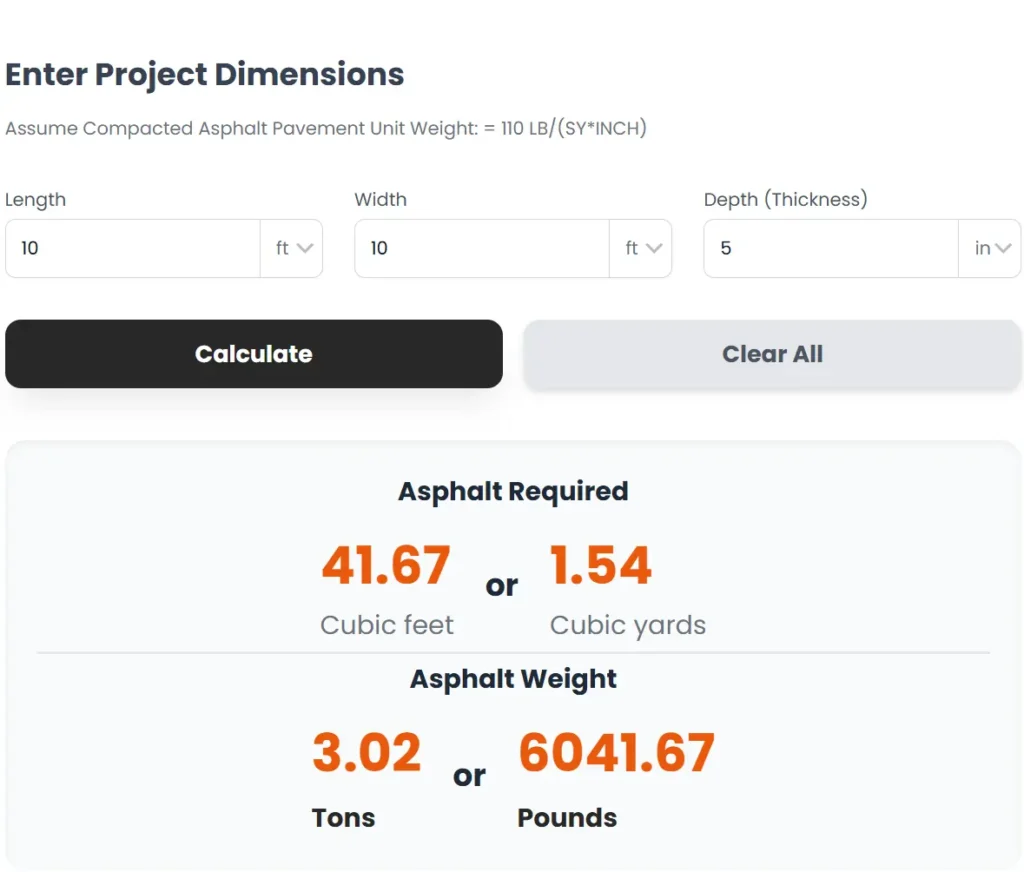
Enter Project Dimensions
Assume Compacted Asphalt Pavement Unit Weight: = 110 LB/(SY*INCH)
A Asphalt calculator is an online tool used to estimate the quantity of paving materials needed for a specific project. This includes materials like pavers, sand, gravel, and sealant. It is designed to simplify the planning process for homeowners and contractors alike, helping them avoid over-ordering or running short of essential supplies.
Table of Contents
Asphalt Tools
Asphalt Area Calculator
Calculate Area of your Asphalt Areaa Calculator
Area Calculator
Asphalt Compaction Calculator
Calculate your Asphalt compaction calculator.
Compaction Calculator
Asphalt Temperature Calculator
Calculate your Asphalt Temperature calculator
Temperature Calculator
Asphalt Cost Per Square Foot Calculator
Calculate Asphalt Cost Per Square Foot
Cost Per Square Foot Calculator
Asphalt Tonnage Calculator
Calculate your Asphalt Tonnage.
Tonnage Calculator
Asphalt Volume Calculator
Calculate your Asphalt Volume Calculator
Volume Calculator
Asphalt Weight Calculator
Calculate Asphalt Weight with it
Weight Calculator
Asphalt Aggregate Calculator
Calculate your Asphalt Aggregate
Aggregate Calculator
Asphalt Driveway Cost Calculator
Calculate your Asphalt Driveway Cost
Driveway Cost Calculator
How to use Asphalt Calculator ?
If you’re interested in broader environmental factors that affect construction materials, you can explore National Geographic’s Environment section for climate-related insights.
Asphalt Calculator Formula
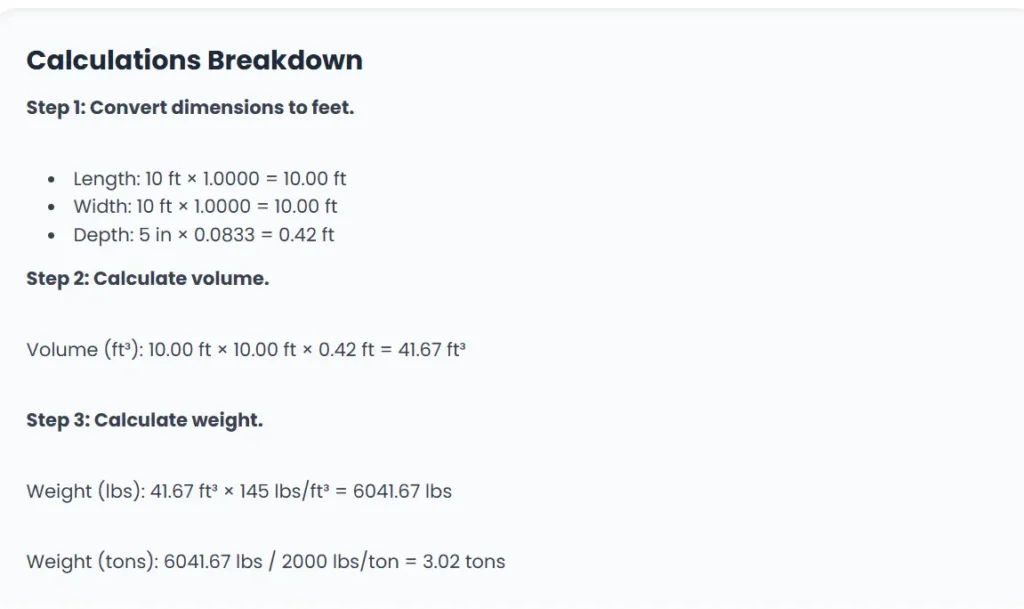
The following explains the steps and information needed to calculate the required asphalt for a paving project. The formulas determine the volume of asphalt in cubic feet and cubic yards, as well as the total weight in pounds and tons.
Volume (ft3)=Length(ft)×Width(ft)×Depth(ft)
Weight(lbs)=Volume(ft3)×Asphalt Density
Variables:
To calculate the asphalt volume, you multiply the length, width, and depth after converting them all to feet. To calculate the weight, you multiply the volume in cubic feet by the asphalt’s density.
How to Calculate Asphalt Requirements
The following steps outline how to use the formulas to find the asphalt you’ll need.
After inserting the variables and calculating the result, you can check your answer with the tool.
Example Problem:
Use the following variables as an example problem to test your knowledge.
Length: 30 ft
Width: 10 ft
Depth: 3 inches
Volumeft3=?
Weighttons=?
Solution:
First, convert the depth to feet: 3/12=0.25 ft.
Next, calculate the volume: 30 ft×10 ft×0.25 ft=75 ft3.
Finally, calculate the weight in tons: (75 ft3×145 lbs/ft3)/2000 lbs/ton=5.44 tons.
How to Estimate Asphalt
Accurately estimating the amount of asphalt needed for any paving project is crucial for staying on schedule and within budget. Miscalculations can lead to costly delays and wasted materials, so it’s essential to get it right.
This guide, along with our new web calculator, provides a comprehensive, step-by-step process for contractors to precisely measure the project area and account for all the factors that influence material requirements.
Guide to Calculating Asphalt Volume
1. Assess the Existing Base
Before you begin, evaluate the condition of the surface you’ll be paving over.
2. Measure the Area
Measure the length and width of the area in feet to calculate the square footage.
3. Calculate the Volume
Once you have the area in square feet and the depth in inches, you can calculate the volume.
Volume(incubicyards)=27Area(sq.ft.)×Depth(ft.)
Example: For a 1,000 sq. ft. area with a 3-inch depth:
Volume=271000sq.ft.×(3/12ft.)≈9.26cubicyards
4. Account for Compaction
Asphalt is compacted during the paving process, which reduces its volume. It’s essential to add a percentage for this compaction to your initial volume calculation to ensure you order enough material.
Example: Using the volume from the previous step:
Volume(withcompaction)=9.26×1.10≈10.19cubicyards
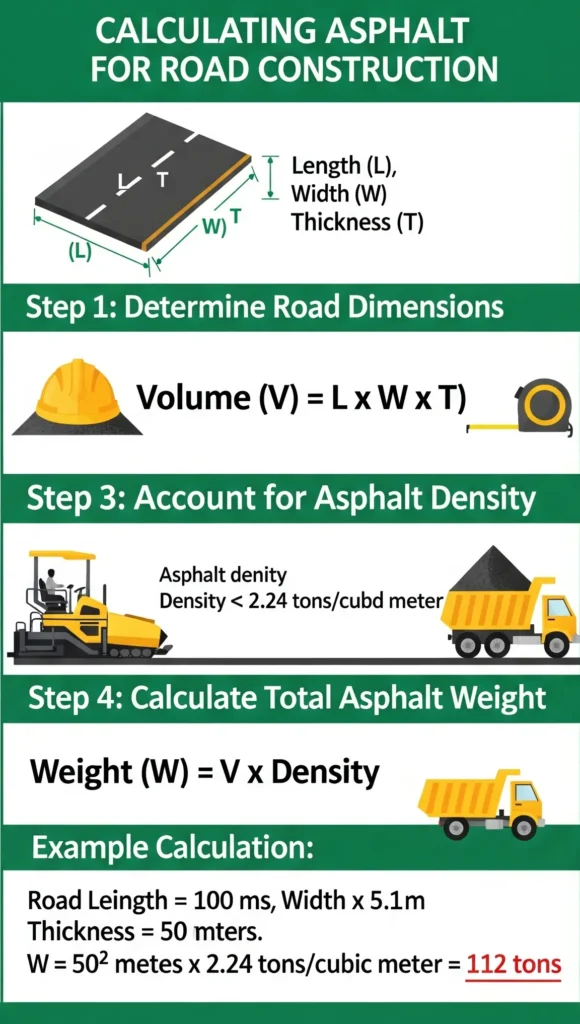
How to Calculate Asphalt for Road
1. Get Road Dimensions:
- Length (L) × Width (W)
- Thickness (T)
2. Calculate Volume:
- Volume = L × W × T (in m3)
3. Convert to Weight:
- Asphalt (tons) = Volume × 2.4
- Asphalt Density = 2.4−2.5 tons/m3
- Or approx. 150 lb/ft3
Example:
- L = 100 m, W = 7 m, T = 0.1 m
- Volume = 100×7×0.1=70 m3
- Weight = 70×2.4=168 tons
✅ Add 5−10% for wastage
Factors Influence Asphalt Quantity
Beyond the basic measurements, several other factors can significantly impact the amount of asphalt you need.
Types of Asphalt Mixes
The type of asphalt mix you choose depends on the project’s specific needs, including its intended use and application. The key differences lie in the selection of aggregates and the temperature at which the asphalt is mixed.
Knowing how to properly calculate your asphalt needs and what type of material to use are two of the most important steps for any successful paving job. Do you have a specific paving project in mind that you need help estimating?
Conclusion
An asphalt calculator is an essential and user-friendly tool that streamlines the planning process for any paving project. By accurately translating project dimensions into concrete figures for volume and weight, it takes the guesswork out of material estimation.
This not only helps you avoid the common pitfalls of under-ordering or over-ordering but also leads to significant savings in both cost and time. Ultimately, whether you’re a DIY enthusiast or a professional, using an asphalt calculator ensures your project is well-planned, efficient, and environmentally friendly by minimizing waste.